The CSS Working Group and the SVG Working Group invite implementations of the Candidate Recommendation of Geometry Interfaces Module Level 1.
This specification provides basic geometric interfaces to represent
points, rectangles, quadrilaterals and transformation matrices that can
be used by other modules or specifications. Learn more about the Style Activity and the Graphics Activity.
Search Engine Marketing| seo tips | w3c Release | Unlock the secrets of SEO success and W3C standards mastery on our blog. Elevate your online presence with expert insights, staying visible and accessible
Friday, November 28, 2014
Filter Effects Module Level 1 Draft Published
25 November 2014
The CSS Working Group and the SVG Working Group have published a Working Draft of Filter Effects Module Level 1.
Filter effects are a way of processing an element’s rendering before it
is displayed in the document. Typically, rendering an element via CSS
or SVG can conceptually be described as if the element, including its
children, are drawn into a buffer (such as a raster image) and then that
buffer is composited into the elements parent. Filters apply an effect
before the compositing stage. Examples of such effects are blurring,
changing color intensity and warping the image. Although originally
designed for use in SVG, filter effects are a set of operations to apply
on an image buffer and therefore can be applied to nearly any
presentational environment, including CSS. They are triggered by a style
instruction (the filter property). This specification describes filters
in a manner that allows them to be used in content styled by CSS, such
as HTML and SVG. It also defines a CSS property value function that
produces a CSS value. Learn more about the Style Activity and the Graphics Activity.
Standards for Web Applications on Mobile: current state and roadmap
20 November 2014
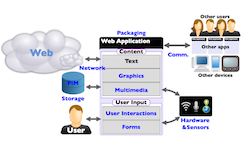 W3C has published the October 2014 edition of Standards for Web Applications on Mobile,
an overview of the various technologies developed in W3C that increase
the capabilities of Web applications, and how they apply more
specifically to the mobile context.
W3C has published the October 2014 edition of Standards for Web Applications on Mobile,
an overview of the various technologies developed in W3C that increase
the capabilities of Web applications, and how they apply more
specifically to the mobile context.A deliverable of the HTML5Apps project, this edition includes changes and additions since July 2014, notably emerging work such as the Second Screen Presentation Working Group API to request display of content on an external screen, a draft API from the Web Bluetooth Community Group, Device APIs Working Group work on a generic pattern for sensors APIs, as well as work on an API to manage permissions across other APIs. Learn more about the Web and Mobile Interest Group.
Friday, October 10, 2014
CSS Regions Module Level 1 Draft Published
The Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) Working Group has published a Working Draft of CSS Regions Module Level 1.
The CSS Regions module allows content from one or more elements to flow
through one or more boxes called CSS Regions, fragmented as defined in
CSS3-BREAK. This module also defines CSSOM to expose both the inputs and
outputs of this fragmentation. CSS is a language for describing the
rendering of structured documents (such as HTML and XML) on screen, on
paper, in speech, etc. Learn more about the Style Activity.
Last Call: XQuery 3.1 and XQueryX 3.1; and additional supporting documents
Today the XQuery Working Group published a Last Call Working Draft of XQuery 3.1 and XQueryX 3.1. Additional supporting documents were published jointly with the XSLT Working Group: a Last Call Working Draft of XPath 3.1, together with XPath Functions and Operators, XQuery and XPath Data Model, and XSLT and XQuery Serialization.
XQuery 3.1 and XPath 3.1 introduce improved support for working with
JSON data with map and array data structures as well as loading and
serializing JSON; additional support for HTML class attributes, HTTP
dates, scientific notation, cross-scaling between XSLT and XQuery and
more. Comments are welcome through 7 November 2014. Learn more about the XML Activity.
Selection API First Public Draft Published; Push API Draft Published
The Web Applications Working Group has published two documents today:
- A First Public Working Draft of Selection API. This document is a preliminary draft of a specification for the Selection API and selection related functionality. It replaces a couple of old sections of the HTML specification, the selection part of the old DOM Range specification.
- A Working Draft of Push API. The Push API provides webapps with scripted access to server-sent messages, for simplicity referred to here as push messages, as delivered by push services. A push service allows a webapp server to send messages to a webapp, regardless of whether the webapp is currently active on the user agent. The push message will be delivered to a Service Worker, which could then store the message’s data or display a notification to the user. This specification is designed to promote compatibility with any delivery method for push messages from push services to user agents.
Sunday, September 21, 2014
Last Call: TriG
20 September 2013
The RDF Working Group has published a Last Call Working Draft of TriG.
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a general-purpose language
for representing information in the Web. This document defines a textual
syntax for RDF called TriG that allows an RDF dataset to be completely
written in a compact and natural text form, with abbreviations for
common usage patterns and datatypes. TriG is an extension of the Turtle
[turtle] format. Comments are welcome through 11 October. Learn more
about the Semantic Web Activity.DOMMatrix interface Draft Published
20 September 2013
The CSS Working Group and the SVG Working Group have published a First Public Working Draft of DOMMatrix interface.
This specification describes a transformation matrix interface with the
dimension of 3x2 and 4x4. The transformation matrix interface replaces
the SVGMatrix interface from SVG. It is a common interface used to
describe 2D and 3D transformations on a graphical context for SVG,
Canvas 2D Context and CSS Transforms. Learn more about the Style Activity and the Graphics ActivityCSS Ruby Module Level 1, and CSS Syntax Module Level 3 Drafts Published
20 September 2013
The Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) Working Group has published two Working Drafts today:- CSS Ruby Module Level 1. “Ruby” are short runs of text alongside the base text, typically used in East Asian documents to indicate pronunciation or to provide a short annotation. This module describes the rendering model and formatting controls related to displaying ruby annotations in CSS. CSS is a language for describing the rendering of structured documents (such as HTML and XML) on screen, on paper, in speech, etc.
- CSS Syntax Module Level 3. This module describes, in general terms, the basic structure and syntax of CSS stylesheets. It defines, in detail, the syntax and parsing of CSS - how to turn a stream of bytes into a meaningful stylesheet.
Wednesday, August 27, 2014
W3C Invites Implementations of CSS Masking Module Level 1
The Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) Working Group and the SVG Working Group invite implementation of the Candidate Recommendation of CSS Masking Module Level 1.
CSS Masking provides two means for partially or fully hiding portions
of visual elements: masking and clipping. Masking describes how to use
another graphical element or image as a luminance or alpha mask.
Clipping describes the visible region of visual elements. The region can
be described by using certain SVG graphics elements or basic shapes.
Anything outside of this region is not rendered. CSS is a language for
describing the rendering of structured documents (such as HTML and XML)
on screen, on paper, in speech, etc. Learn more about the Style Activity and the Graphics Activity.
Last Call: CSS Counter Styles Level 3
The Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) Working Group has published a Last Call Working Draft of CSS Counter Styles Level 3. This module introduces the
@counter-style
rule, which allows authors to define their own custom counter styles
for use with CSS list-marker and generated-content counters. It also
predefines a set of common counter styles, including the ones present in
CSS2 and CSS2.1. Comments are welcome through 23 September.
CSS is a language for describing the rendering of structured documents
(such as HTML and XML) on screen, on paper, in speech, etc. Learn more
about the Style Activity.Friday, August 1, 2014
W3C Invites Implementations of HTML5
The HTML Working Group invites implementation of the Candidate Recommendation of HTML5.
This specification defines the 5th major revision of the core language
of the World Wide Web: the Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). In this
version, new features are introduced to help Web application authors,
new elements are introduced based on research into prevailing authoring
practices, and special attention has been given to defining clear
conformance criteria for user agents in an effort to improve
interoperability. Learn more about the HTML Activity.
For Review: Updated Techniques for Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines Working Group (WCAG WG) requests review of draft updates to Notes that accompany WCAG 2.0: Techniques for WCAG 2.0 (Editors’ Draft) and Understanding WCAG 2.0 (Editors’ Draft). Comments are welcome through 12 August 2014. (This is not an update to WCAG 2.0, which is a stable document.) To learn more about the updates, see the Call for Review: WCAG 2.0 Techniques Draft Updates e-mail. Read about the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).
Thursday, June 26, 2014
Last Call: Beacon, Resource Timing Candidate Recommendation Updated
The Web Performance Working Group has published a Last Call Working Draft of Beacon.
This specification defines an interoperable means for site developers
to asynchronously transfer small HTTP data from the User Agent to a web
server. Comments are welcome through 29 July 2014.
The Web Performance Working Group also updated the Candidate Recommendation of Resource Timing. This specification defines an interface for web applications to access the complete timing information for resources in a document.
Learn more about the Rich Web Client Activity.
The Web Performance Working Group also updated the Candidate Recommendation of Resource Timing. This specification defines an interface for web applications to access the complete timing information for resources in a document.
Learn more about the Rich Web Client Activity.
RDF 1.1 Primer Note Published
The RDF Working Group has published a Group Note of RDF 1.1 Primer.
This primer is designed to provide the reader with the basic knowledge
required to effectively use RDF. It introduces the basic concepts of RDF
and shows concrete examples of the use of RDF. Learn more about the Data Activity.
RDF 1.1 Primer Note Published
The RDF Working Group has published a Group Note of RDF 1.1 Primer.
This primer is designed to provide the reader with the basic knowledge
required to effectively use RDF. It introduces the basic concepts of RDF
and shows concrete examples of the use of RDF. Learn more about the Data Activity.
Tuesday, May 27, 2014
Emotion Markup Language (EmotionML) 1.0 is a W3C Recommendation
The Multimodal Interaction Working Group has published a W3C Recommendation of Emotion Markup Language (EmotionML) 1.0.
As the Web is becoming ubiquitous, interactive, and multimodal,
technology needs to deal increasingly with human factors, including
emotions. The specification of Emotion Markup Language 1.0 aims to
strike a balance between practical applicability and scientific
well-foundedness. The language is conceived as a “plug-in” language
suitable for use in three different areas: (1) manual annotation of
data; (2) automatic recognition of emotion-related states from user
behavior; and (3) generation of emotion-related system behavior. Learn
more about the Multimodal Interaction Activity.
vCard Ontology for describing People and Organizations Note Published
The Semantic Web Interest Group has published a new version of the Interest Group Note for the vCard Ontology.
The document describes a mapping of the vCard specification (RFC6350)
to RDF/OWL. The goal is to promote the use of vCard for the description
of people and organizations utilizing semantic web techniques and
allowing compatibility with traditional vCard implementations. Learn
more about the Data Activity.
Last Call: CSS Font Loading Module Level 3
The Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) Working Group has published a Last Call Working Draft of CSS Font Loading Module Level 3.
This CSS module describes events and interfaces used for dynamically
loading font resources. CSS is a language for describing the rendering
of structured documents (such as HTML and XML) on screen, on paper, in
speech, etc. Comments are welcome through 30 June 2014. Learn more about the Style Activity.
First Public Working Draft of Geometry Interfaces Module Level 1, Last Call: CSS Masking Module Level 1
The Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) Working Group and the SVG Working Group have published two documents today:
- A First Public Working Draft of Geometry Interfaces Module Level 1. This specification describes several geometry interfaces for the representation of points, quads, rectangles and transformation matrices. The SVG interfaces are aliasing the interfaces in favor for common interfaces used by SVG, Canvas 2D Context and CSS Transforms.
- A Last Call Working Draft of CSS Masking Module Level 1. CSS Masking provides two means for partially or fully hiding portions of visual elements: masking and clipping. Masking describes how to use another graphical element or image as a luminance or alpha mask. Clipping describes the visible region of visual elements. The region can be described by using certain SVG graphics elements or basic shapes. Anything outside of this region is not rendered. Comments are welcome through 19 June 2014.
Thursday, April 17, 2014
SVG Integration Draft Published
The SVG Working Group has published a Working Draft of SVG Integration.
This specification details requirements on how SVG documents must be
processed when used in various contexts, such as CSS background images,
HTML ‘iframe’ elements, and so on. These requirements include which
features are restricted or disabled, such as scripting and animation. A
number of referencing modes are defined, which other specifications that
allow the embedding or referencing of SVG documents can normatively
reference. Learn more about the Graphics Activity.
XML Entity Definitions for Characters (2nd Edition), and Mathematical Markup Language (MathML) Version 3.0 2nd Edition are W3C Recommendations
The Math Working Group has published two W3C Recommendations today:
- XML Entity Definitions for Characters (2nd Edition). This document defines several sets of names, so that to each name is assigned a Unicode character or sequence of characters. Each of these sets is expressed as a file of XML entity declarations.
- Mathematical Markup Language (MathML) Version 3.0 2nd Edition. This specification defines the Mathematical Markup Language, or MathML. MathML is a markup language for describing mathematical notation and capturing both its structure and content. The goal of MathML is to enable mathematics to be served, received, and processed on the World Wide Web, just as HTML has enabled this functionality for text.
Tuesday, March 25, 2014
Thursday, March 13, 2014
Metadata API for Media Resources 1.0 is a W3C Recommendation
The Media Annotations Working Group published a Recommendation of Metadata API for Media Resources 1.0.
This document defines an API to access metadata information related to
media resources on the Web. The overall purpose is to provide developers
with a convenient access to metadata information stored in different
metadata formats. The API provides means to access the set of metadata
properties defined in the Ontology for Media Resources 1.0
specification. Learn more about the Video on the Web Activity.
W3C Invites Implementations of State Chart XML (SCXML): State Machine Notation for Control Abstraction
The Voice Browser Working Group invites implementation of the Candidate Recommendation of State Chart XML (SCXML): State Machine Notation for Control Abstraction.
This document describes SCXML, or the “State Chart extensible Markup
Language”. SCXML provides a generic state-machine based execution
environment based on CCXML and Harel State Tables. Learn more about the Voice Browser Activity.
Linked Data Platform Use Cases and Requirements Note Published
The Linked Data Platform (LDP) Working Group has published a Group Note of Linked Data Platform Use Cases and Requirements.
To foster the development of the Linked Data Platform specification,
this document includes a set of user stories, use cases, scenarios and
requirements that motivate a simple read-write Linked Data architecture,
based on HTTP access to web resources that describe their state using
RDF. The aim throughout has been to avoid details of protocol
(specifically the HTTP protocol), and use of any specific vocabulary
that might be introduced by the LDP specification. Learn more about the Data Activity.
First Public Working Drafts of Annotation Use Cases, Requirements for Latin Text Layout and Pagination
The Digital Publishing Interest Group has published two First Public Working Drafts :
- Annotation Use Cases, which describes the set of use cases generated for Annotation and Social Reading within the W3C Digital Publishing Interest Group, in coordination with the Open Annotation Community Group.
- Requirements for Latin Text Layout and Pagination, which describes requirements for pagination and layout of books in latin languages, based on the tradition of print book design and composition. It is hoped that these principles can inform the pagination of digital content as well, and serve as a reference for the CSS Working Group and other interested parties. This work was inspired by JLREQ.
Monday, February 17, 2014
Facebook Fans for your website
By Seomul Evans
For many businesses and institutions, having a Facebook page is an effective way to promote their products and services, and can significantly expand their network. Getting tons of fans on Facebook is easy, if you just follow some of these simple ideas.
First off, start with what you already have. Click on the "Suggest to Friends" button and invite friends from your original profile. The number of fans you will get from this method depends mainly on the number of friends that you actually have and your relationship with them. Aside from this, you should also invite your e-zine and e-mail subscribers. Send out an e-mail to your subscribers informing them of your fan page, and place a logo of Facebook in your newsletters.
Get the people who regularly visit your site to go to your Facebook fan page by embedding eye-catching things on your website. Choose from a number of widgets that you can embed on your site, such as the Fan Box widget, where you can display your page stream and some fans, or the Live Stream widget, which fans can use to send comments in real time. You can also load nice videos on your Facebook page and embed them on your website or your blog. The video serves as a link to your Facebook fan page.
People are attracted to unique and interesting material. A great way to get more people to check out your Facebook page and like it is to add interesting stuff on your fan page. Make your fan page unique by uploading an attractive welcome video on your main canvas page. Here, you can share what your page is about and why people should "Like" it. There are also a number of Facebook applications that you can try adding to your page to make it more appealing, such as Vpype, a live video-streaming application where you can air Internet shows directly from your page. There are also several companies that create custom Facebook applications, depending on what you want.
After doing this you post interesting updates, articles and news relevant to your business on your Facebook, so that people who are added in your list get the post and are forced to comment on your profile. By doing this the user who will comment on your profile will in return automatically post your comment to all users in his profile. This will notify more users about your existence and you will end up getting more people in your network.
Don't forget to link, link, link. Make sure you add a link on your personal profile page that will direct your visitors to your Facebook fan page. Place your fan page’s URL right below your profile picture, on the "Write something about yourself" area, so that it will be easily visible to friends who visit your page. You can also link your fan page to other sites, such as Twitter. Your Facebook updates will automatically get posted to your Twitter account, and you can also promote your fan page on your background and Twitter bio field.
Above are the ways of doing it but the most important thing is that you keep on posting on your Facebook profile. You have to be very active on Facebook. An active profile is the key to attracting more and more users.
These are only a few of the things you can do to increase your Facebook fans. Try them out!
About the Author: Seomul Evans is a senior Custom Facebook Fan page designer and a Social Media Blogger.
Source: www.isnare.com
For many businesses and institutions, having a Facebook page is an effective way to promote their products and services, and can significantly expand their network. Getting tons of fans on Facebook is easy, if you just follow some of these simple ideas.
First off, start with what you already have. Click on the "Suggest to Friends" button and invite friends from your original profile. The number of fans you will get from this method depends mainly on the number of friends that you actually have and your relationship with them. Aside from this, you should also invite your e-zine and e-mail subscribers. Send out an e-mail to your subscribers informing them of your fan page, and place a logo of Facebook in your newsletters.
Get the people who regularly visit your site to go to your Facebook fan page by embedding eye-catching things on your website. Choose from a number of widgets that you can embed on your site, such as the Fan Box widget, where you can display your page stream and some fans, or the Live Stream widget, which fans can use to send comments in real time. You can also load nice videos on your Facebook page and embed them on your website or your blog. The video serves as a link to your Facebook fan page.
People are attracted to unique and interesting material. A great way to get more people to check out your Facebook page and like it is to add interesting stuff on your fan page. Make your fan page unique by uploading an attractive welcome video on your main canvas page. Here, you can share what your page is about and why people should "Like" it. There are also a number of Facebook applications that you can try adding to your page to make it more appealing, such as Vpype, a live video-streaming application where you can air Internet shows directly from your page. There are also several companies that create custom Facebook applications, depending on what you want.
After doing this you post interesting updates, articles and news relevant to your business on your Facebook, so that people who are added in your list get the post and are forced to comment on your profile. By doing this the user who will comment on your profile will in return automatically post your comment to all users in his profile. This will notify more users about your existence and you will end up getting more people in your network.
Don't forget to link, link, link. Make sure you add a link on your personal profile page that will direct your visitors to your Facebook fan page. Place your fan page’s URL right below your profile picture, on the "Write something about yourself" area, so that it will be easily visible to friends who visit your page. You can also link your fan page to other sites, such as Twitter. Your Facebook updates will automatically get posted to your Twitter account, and you can also promote your fan page on your background and Twitter bio field.
Above are the ways of doing it but the most important thing is that you keep on posting on your Facebook profile. You have to be very active on Facebook. An active profile is the key to attracting more and more users.
These are only a few of the things you can do to increase your Facebook fans. Try them out!
About the Author: Seomul Evans is a senior Custom Facebook Fan page designer and a Social Media Blogger.
Source: www.isnare.com
W3C Training: Early Bird Rates through 27 February for JavaScript and HTML5 Courses
W3C is pleased to launch a new edition of its JavaScript online course,
to help Web developers master good JavaScript practices and avoid the
pitfalls of the language. The course is 4 weeks long, to start on 17
March 2014. This course is a condensed set of tricks, advice, tools and
good practices built around JavaScript, with a logical flow that is
always illustrated by examples and assignments. JavaScript is one of the
three major Web developer tools, along with HTML5 and CSS3, so register before February 27 to benefit from the early bird rate.
Register now to the upcoming W3C HTML5 online course, to start 27 March 2014. Acclaimed trainer Michel Buffa will cover the techniques developers and designers need to create great Web pages and apps. This course edition features additional advanced sections on time based animation, 2D geometric transformations, Web Audio API, etc., all illustrated by numerous examples. Register before February 27 to benefit from the early bird rate.
Learn more about W3DevCampus, the W3C online training for Web developers.
Register now to the upcoming W3C HTML5 online course, to start 27 March 2014. Acclaimed trainer Michel Buffa will cover the techniques developers and designers need to create great Web pages and apps. This course edition features additional advanced sections on time based animation, 2D geometric transformations, Web Audio API, etc., all illustrated by numerous examples. Register before February 27 to benefit from the early bird rate.
Learn more about W3DevCampus, the W3C online training for Web developers.
Labels:
CSS3,
html5,
javascript,
register now,
w3c,
W3DevCampus
Friday, February 14, 2014
CSS Masking Module Level 1 Draft Published
The CSS Working Group and the SVG Working Group have published a Working Draft of CSS Masking Module Level 1.
CSS Masking provides two means for partially or fully hiding portions
of visual elements: masking and clipping. Masking describes how to use
another graphical element or image as a luminance or alpha mask.
Typically, rendering an element via CSS or SVG can conceptually be
described as if the element, including its children, are drawn into a
buffer and then that buffer is composited into the element’s parent.
Luminance and alpha masks influence the transparency of this buffer
before the compositing stage. Clipping describes the visible region of
visual elements. The region can be described by using certain SVG
graphics elements or basic shapes. Anything outside of this region is
not rendered. CSS is a language for describing the rendering of
structured documents (such as HTML and XML) on screen, on paper, in
speech, etc. Learn more about the Style Activity and the Graphics Activity.
Progress Events is a W3C Recommendation
The Web Applications Working Group has published a W3C Recommendation of Progress Events.
The Progress Events specification defines an event interface that can
be used for measuring progress; e.g. HTTP entity body transfers. This
specification is primarily meant to be used by other specifications.
Learn more about the Rich Web Client Activity.
Efficient XML Interchange (EXI) Format 1.0 (Second Edition) is a W3C Recommendation
The Efficient XML Interchange Working Group has published a W3C Recommendation of Efficient XML Interchange (EXI) Format 1.0 (Second Edition).
This document is the specification of the Efficient XML Interchange
(EXI) format. EXI is a very compact representation for the Extensible
Markup Language (XML) Information Set that is intended to simultaneously
optimize performance and the utilization of computational resources.
The EXI format uses a hybrid approach drawn from the information and
formal language theories, plus practical techniques verified by
measurements, for entropy encoding XML information. Using a relatively
simple algorithm, which is amenable to fast and compact implementation,
and a small set of datatype representations, it reliably produces
efficient encodings of XML event streams. The grammar production system
and format definition of EXI are presented. Learn more about the Extensible Markup Language (XML) Activity.
Friday, February 7, 2014
Call for Review: Accessible Rich Internet Applications (WAI-ARIA) 1.0 advances to Proposed Recommendation
The Protocols and Formats Working Group (PFWG) today published Accessible Rich Internet Applications (WAI-ARIA) 1.0 and the WAI-ARIA 1.0 User Agent Implementation Guide
as Proposed Recommendations. WAI-ARIA is a technical specification for
making dynamic, interactive Web content accessible to people with
disabilities. WAI-ARIA and supporting documents are described in the WAI-ARIA Overview. Comments are welcome by 7 March 2014. More information is provided in the WAI-ARIA 1.0 is Proposed Recommendation e-mail. Read about the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).
XML processor profiles Note Published
The XML Processing Model Working Group has published a Working Group Note of XML processor profiles.
This specification defines several XML processor profiles, each of
which defines how any given XML document should be processed, both
operationally and in terms of what information must be made available to
applications. It is intended as a resource for other specifications,
which can by a single normative reference establish precisely what input
processing they require as well as what information they require. Learn
more about the Extensible Markup Language (XML) Activity.
Tuesday, January 28, 2014
Reminder: Position Papers for W3C Workshop on Web Payments due 8 February
W3C invites the financial technology community to attend its Workshop Web Payments: How do you want to pay?,
on March 24-25 in Paris, France. W3C Member and non-Member participants
will include banks, credit card companies, governments, mobile network
operators, payment solution providers, technology companies, retailers,
and content creators. W3C’s Workshop goal is to leverage the power of
the Web to improve consumer payment choice and satisfaction, while
easing the work of web developers to support all current and future
payment solutions and empowering payment providers to easily reach
across different solutions, devices and platforms. There is no Workshop
fee, but interested parties should submit a presentation proposal or
statement of interest to the Workshop Program Committee by 8 February.
Read the media advisory and more information on participation.
Updated Drafts of Tracking Preference Expression (DNT), and Tracking Compliance and Scope
The Tracking Protection Working Group has published two documents today.
- A Working Draft Tracking Preference Expression (DNT). This specification defines the DNT request header field as an HTTP mechanism for expressing the user’s preference regarding tracking, an HTML DOM property to make that expression readable by scripts, and APIs that allow scripts to register site-specific exceptions granted by the user. It also defines mechanisms for sites to communicate whether and how they honor a received preference through use of the Tk response header field and well-known resources that provide a machine-readable tracking status.
- A Working Draft of Tracking Compliance and Scope. This specification defines the meaning of a Do Not Track (DNT) preference and sets out practices for websites to comply with this preference.
Thursday, January 23, 2014
CSS Grid Layout Module Level 1 Working Draft Updated
The CSS Working Group has published an updated Working Draft of CSS Grid Layout Module Level 1.
This CSS module defines a two-dimensional grid-based layout system,
optimized for user interface design. In the grid layout model, the
children of a grid container can be positioned into arbitrary slots in a
flexible or fixed predefined layout grid. CSS is a language for
describing the rendering of structured documents (such as HTML and XML)
on screen, on paper, in speech, etc. Learn more about the Style Activity.
Tuesday, January 14, 2014
Web NFC API is a First Public Working Draft
The NFC Working Group has published a First Public Working Draft of Web NFC API.
Near Field Communication (NFC) is an international standard (ISO/IEC
18092) that specifies an interface and protocol for simple wireless
interconnection of closely coupled devices operating at 13.56 MHz. NFC
enables wireless communication between two devices at close proximity,
usually less than a few centimeters, according to three groups of
scenarios; holding a device close to a wireless tag to exchange some
digital information or data, holding two devices close to each other in
order to exchange some information or data between them, making payments
by holding mobile phones close to point of sales terminals instead of
swiping smart cards. Learn more about the Ubiquitous Web Applications Activity.
Thursday, January 9, 2014
Learn how to program Web applications with W3C’s Mobile Web 2 online course
Registration is open for W3C’s online course Mobile Web 2: Programming Applications. The course starts 13 January 2014
and runs through 23 February. This course covers all techniques for
programming successful mobile Web applications that can ship both online
and in application stores. Participants have access to high quality
content material and step-by-step instruction from expert Niall Roche. Learn more about W3DevCampus, W3C’s online training for Web developers.
Introduction to Model-Based User Interfaces and MBUI Glossary Published as Group Notes
The MBUI Working Group has published two Working Group Notes.
- Introduction to Model-Based User Interfaces, as an introduction to Model-Based User Interfaces covering the benefits and shortcomings of the model-based approach, a collection of use cases, and terminology.
- MBUI – Glossary, a glossary of terms recurrent in the Model-based User Interfaces domain. It is intended to capture a common, coherent terminology for specifications of the MBUI Working Group and to provide a concise reference of domain terms for interested audience.
Last Call: Compositing and Blending Level 1
The CSS Working Group and the SVG Working Group have published a Last Call Working Draft of Compositing and Blending Level 1.
Compositing describes how shapes of different elements are combined
into a single image. Previous versions of SVG and CSS used Simple Alpha
Compositing. In this model, each element is rendered into its own buffer
and is then merged with its backdrop using the Porter Duff source-over
operator. This specification defines a new compositing model that
expands upon the Simple Alpha Compositing model by offering additional
Porter Duff compositing operators; advanced blending modes which allow
control of how colors mix in the areas where shapes overlap; and
compositing groups. In addition, this specification defines CSS
properties for blending and group isolation, and defines the
‘globalcompositeoperation’ as specified in HTML Canvas 2D Context, Level
2. Comments are welcome by 28 January 2014. Learn more about the Style Activity and the Graphics Activity.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)